 I. Introduction
I. Introduction The DFA staining technique is used to detect viruses either directly in patient specimens or which have been isolated in shell vial or tube cultures. The method consists of a single staining step using a virus-specific antibody which is conjugated with a fluorochrome. Viruses which we currently identify by DFA staining include HSV-1, HSV-2, VZV, CMV (late antigen) and respiratory viruses (SimulFluor stains for respiratory syncytial virus, parainfluenza, influenza, adenovirus).
http://bahankuliahkesehatan.blogspot.com/
II. Reagents and Materials
FITC-conjugated virus-specific antibody
FITC/Rodamine-conjugated virus-specific antibody (SimulFluor)
Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS)
dH2O
cold acetone (4oC)
mounting fluid
sterile pipettes
cytospin and accessories (for tube culture)
humidified chamber
glass slides
coverslips
paper towels for blotting
III. Procedure
1. Shell Vial
This procedure is for staining of cells directly in shell vial. If staining a cytospin slide or slide made directly from a patient specimen, follow the tube culture procedure below.
i. Discard cap. Remove maintenance medium from the shell vial using sterile pipette.
ii. Add 1 mL of cold acetone. Cover with tray lid and let sit for 10 minutes.
iii. Decant acetone and blot shell vial on paper towel.
iv. Gently rinse with PBS from squirt bottle, filling vial 3/4 full. Decant PBS.
v. Add 75ml (2 drops from bottle) of appropriate FITC or Rodamine-conjugated virus-specific antibody. Cover with tray lid.
vi. Incubate at 36oC for 30 minutes.
vii. Gently rinse with PBS from squirt bottle, filling vial 3/4 full. Decant PBS. Repeat.
viii. Remove the coverslip from each shell vial and place cell side down onto a drop of mounting fluid on a glass slide.
ix. For HSV 1, HSV 2, VZ and CMV, read using fluorescence microscope with the FITC/Evans Blue filter and the 40x objective.
x. For respiratory viruses, read using fluorescence microscope with the FITC/Evans Blue Rodamine bi-filter and the 40x objective.
2. Tube Culture
i. Prepare cytospin slide from cell culture tube as outlined in Appendix XX.
ii. Fix slide in cold acetone for 10 minutes in a coplin jar. Remove slide and air dry.
iii. Add 20ml of appropriate FITC or Rodamine -conjugated antibody onto the fixed cytospin slide.
iii. Incubate in a humidified chamber at 36oC for 30 minutes.
iv. Wash each slide 3 times with fresh PBS for 2 minutes each in a coplin jar.
v. Wash with distilled water for 1 minute in a coplin jar.
vi. Wipe excess water from the slide without touching the cytospin preparation.
vii. Mount using coverslip and mounting fluid.
xi. For HSV 1, HSV 2, VZ and CMV, read using fluorescence microscope with the FITC/Evans Blue filter and the 40x objective.
viii. For respiratory viruses, read using fluorescence microscope with the FITC/Evans Blue Rodamine bi-filter.
Interpretation of Results
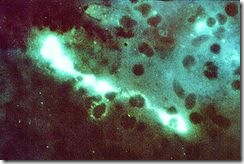
Positive: Bartel CMV monoclonal antibody: Bright apple green fluorescence of cytoplasmic inclusion (late antigen) and homogenous early nuclear antigen in CMV-CPE cells.
Chemicon SimulFluor Respiratory Screen:
All respiratory viruses except RSV show bright apple green fluorescence of the cytoplasm and/or nucleus of the infected cell.
RSV shows bright gold fluorescence of the cytoplasm and/or nucleus of the infected cell.
Chemicon SimulFluor Flu A/Flu B:
Influenzae A virus shows bright apple green fluorescence.
Influenzae B virus shows bright gold fluorescence.
Chemicon SimulFluor RSV/Para 3:
RSV virus shows bright apple green fluorescence.
Parainfluenzae 3 shows bright gold fluorescence.
Chemicon SimulFluor Para 123/Adeno:
Parainfluenza 1,2,3 viruses show bright apple green fluorescence.
Adenovirus shows bright gold fluorescence.
Chemicon individual monoclonal antibodies:
Parainfluenzae 1 and 2, and adenovirus show bright apple green fluorescence.
Negative: Red Cells with no apple-green fluorescence.
IV. Quality Control
Appropriate positive and negative control slides should be stained with each batch.
VI. Reference
Isenberg, H.D., 1992, ASM. Clinical Microbiology Procedures Handbook Vol. 2.
Tidak ada komentar:
Posting Komentar